Auto Cropping- Based on labeling the connected components
This post is about labeling the connected components in a binary image and crop the connected components based on the label. The main two functions used for this simple operation are ‘bwlabel’ and ‘regionprops’.
I used ‘bwlabel’ to label the connected components. After labeling, I used ‘regionprops’ function to find the rectangle containing the region. To find the rectangle points, I used ‘BoundingBox’ property.Then the labeled components are automatically cropped and the image is displayed. To crop an image, ‘imcrop’ function is used.
MATLAB CODE:
A=imread('coins.png');
figure,imshow(A); title('Original Image');

%Convert the Image to binary
B=im2bw(A);
%Fill the holes
C=imfill(B,'holes');
%Label the connected components
[Label,Total]=bwlabel(C,8);
figure,imshow(C); title('Labelled Image');
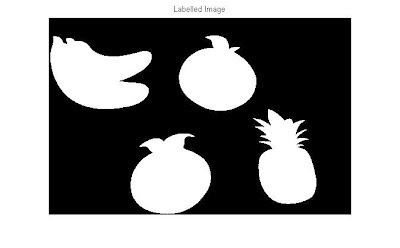 |
| Add caption |
%Rectangle containing the region
Sdata=regionprops(Label,'BoundingBox');
%Crop all the Coins
for i=1:Total
Img=imcrop(A,Sdata(i).BoundingBox);
Name=strcat('Object Number:',num2str(i));
figure,imshow(Img); title(Name);
end


Bit-Plane Slicing
Digitally, an image is represented in terms of pixels.
These pixels can be expressed further in terms of
bits.
Consider the image ‘coins.png’ and the pixel
representation of the image.

Consider the pixels that are bounded within the
yellow line. The binary formats for those values are (8-bit representation)

The binary format for the pixel value 167 is
10100111
Similarly, for 144 it is 10010000
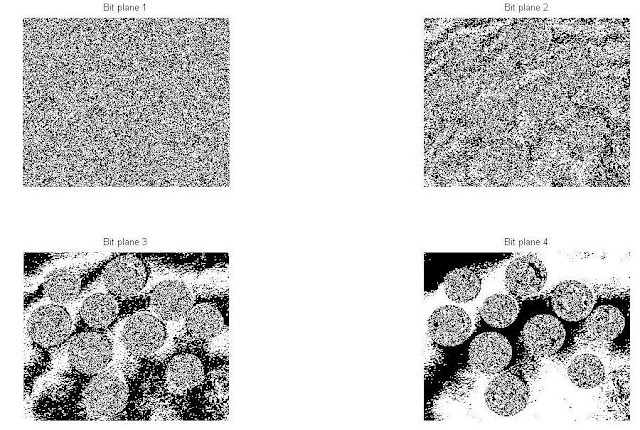
This 8-bit image is composed of eight 1-bit planes.
Plane 1 contains the lowest order bit of all the
pixels in the image.

And plane 8 contains the highest order bit of all
the pixels in the image.

Let’s see how we can do this using MATLAB
A=[167 133 111
144 140 135
159 154 148]
B=bitget(A,1);
%Lowest order bit of all pixels
‘bitget’ is a MATLAB function used to fetch a bit from the specified position from all the
pixels.
B=[1 1 1
0 0 1
1 0 0]
B=bitget(A,8);%Highest order bit of all pixels
B=[1 1 0
1 1 1
1 1 1]
MATLAB CODE:
%Bit Planes from 1 to 8. Output Format: Binary
A=imread('coins.png');
B=bitget(A,1);
figure,
subplot(2,2,1);imshow(logical(B));title('Bit
plane 1');
B=bitget(A,2);
subplot(2,2,2);imshow(logical(B));title('Bit
plane 2');
B=bitget(A,3);
subplot(2,2,3);imshow(logical(B));title('Bit
plane 3');
B=bitget(A,4);
subplot(2,2,4);imshow(logical(B));title('Bit
plane 4');
B=bitget(A,5);
figure,
subplot(2,2,1);imshow(logical(B));title('Bit
plane 5');
B=bitget(A,6);
subplot(2,2,2);imshow(logical(B));title('Bit
plane 6');
B=bitget(A,7);
subplot(2,2,3);imshow(logical(B));title('Bit
plane 7');
B=bitget(A,8);
subplot(2,2,4);imshow(logical(B));title('Bit
plane 8');

Image reconstruction using n bit planes.
1. The
nth plane in the pixels are multiplied by the constant 2^n-1
2. For
instance, consider the matrix
A= A=[167 133 111
144 140 135
159 154 148] and the
respective bit format

3. Combine
the 8 bit plane and 7 bit plane.
For 10100111, multiply the 8 bit
plane with 128 and 7 bit plane with 64.
(1x128)+(0x64)+(1x0)+(0x0)+(0x0)+(1x0)+(1x0)+(1x0)=128
4. Repeat
this process for all the values in the matrix and the final result will be
[128 128 64
128 128 128
128 128 128]
MATLAB CODE:
%Image reconstruction
by combining 8 bit plane and 7 bit plane
A=imread('coins.png');
B=zeros(size(A));
B=bitset(B,7,bitget(A,7));
B=bitset(B,8,bitget(A,8));
B=uint8(B);
figure,imshow(B);
 |
| Image reconstructed using 8 and 7 bit planes |
Explanation:
‘bitset’ is used to
set a bit at a specified position. Use ‘bitget’
to get the bit at the positions 7 and 8 from all the pixels in matrix A and use
‘bitset’ to set these bit values at the positions 7 and 8 in the matrix B.
%Image
reconstruction by combining 8,7,6 and 5 bit planes
A=imread('coins.png');
B=zeros(size(A));
B=bitset(B,8,bitget(A,8));
B=bitset(B,7,bitget(A,7));
B=bitset(B,6,bitget(A,6));
B=bitset(B,5,bitget(A,5));
B=uint8(B);
figure,imshow(B);
 |
| Image reconstructed using 5,6,7 and 8 bit planes |
Find Area, Perimeter, Centroid, Equivdiameter, Roundness and Bounding Box without Using MATLAB Function ‘regionprops’
In MATLAB, the function ‘regionprops’ is used to
measure the image properties. Here are some basic properties computed without
using the function.
Read
an image and find the connected components using ‘bwlabel’ function.
Using the Labeled matrix as an input, the properties
can be measured.
Example:
A=[1 0 0 1
1 1 1 1
0 0 1 1]
To find Area:
· The total number of ‘ON’ pixels in the image.
The number of ones in the matrix is 8.
To find Centroid:
·
Find the row and column having pixel
value one. Eg.[row,column]=find(label==1)
Row=[ 1 2
2 2 3
1 2 3]
Column=[ 1 1
2 3 3
4 4 4]
·
Find the mean of the row and column
having pixel value one.
Mean of Row=2 and mean of column=
2.75
To find the Bounding Box:
·
We need 4 points, starting position(x,y)
, length and breadth.
·
Minimum value of row and column minus
0.5 gives starting position(x,y) respectively
·
Minimum value of row=1-0.5=0.5
·
Minimum value of column=1-0.5=0.5
·
Maximum value of column – minimum value
of column+1 gives breadth of the box
·
Maximum value of column=4
·
Max value-min value of column=3+1
·
Maximum value of row- minimum value of
row +1gives length of the box
·
maximum value of row=3
·
Max value – Min value=2+1
·
Bounding Box value for the given
example:0.5000 0.5000 4.0000
3.0000
·
For more details on how to draw a
rectangle check here: http://angeljohnsy.blogspot.in/2011/06/how-to-draw-in-matlab.html
To find the Perimeter
·
Find the boundary of the labeled
component
Boundary pixels:
1 1
2 2
2 3
1 4
2 4
3 4
3 3
2 2
2 1
1 1
·
Find the distance between the each adjoining pair of pixels around the border of the region.
·
For instance, calculate the distance
between the two points (1,1) and (2,2). distance=sqrt((2-1).^2+(2-1).^2)=1.41
·
Similarly, the distance is computed for
all the pixel positions.
·
The perimeter for the given example is
10.2426
To find the Roundness:
·
Roundness of an object can be determined using the
formula:
Roundness=(4*Area*pi)/(Perimeter.^2)
If the Roundness is greater than 0.90 then, the object is circular in shape.
If the Roundness is greater than 0.90 then, the object is circular in shape.
Result= (4*8*3.14)/10.2426.^2=0.9582
To find the Equivdiameter
·
Formula: sqrt(4*Area/pi).
Equivdiameter for the given example:3.1915







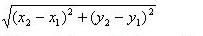
No comments:
Post a Comment